About Ovarian Vein Embolisation
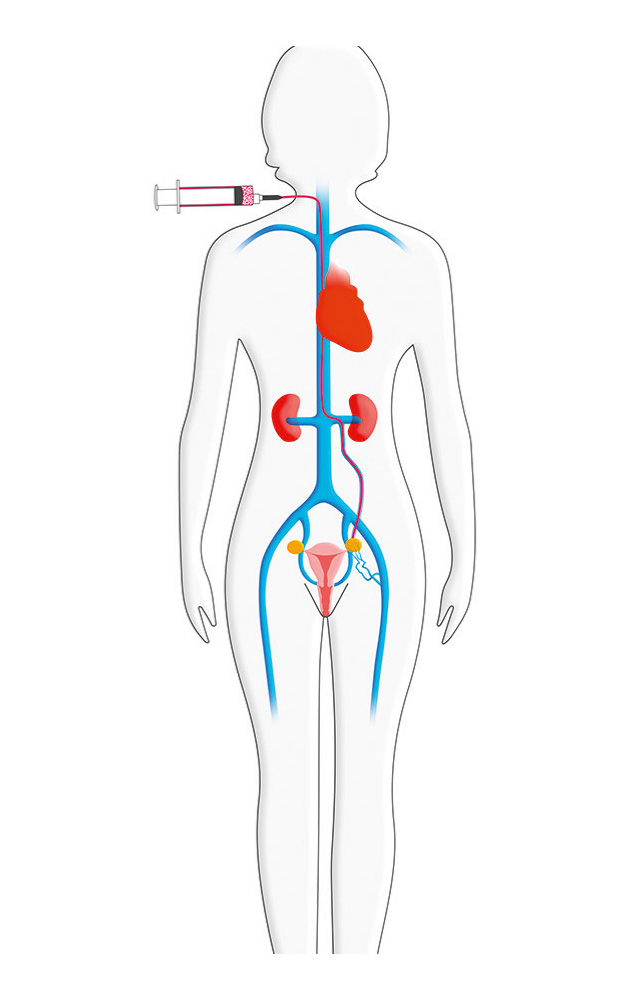
The procedure starts with the patient lying on a radiological table. The patient is usually awake but sedated with a medication that makes them drowsy and feeling no pain.
A small opening is made in the femoral or jugular vein, through which a thin catheter is inserted. The catheter is guided through the venous tree to the pelvis while the Surgeon watches the progress of the procedure using x-ray guided venography.
A venogram is performed by injecting contrast solution into the veins of interest.
During this procedure, the treating doctor will assess the size of the veins , if they are functioning properly and if there is any type of obstruction.6
If the diagnosis of Pelvic Venous Incompetence is confirmed with the venogram, coils will be placed in the abnormal veins. The coils act like small springs, causing blood to clot around them, subsequently blocking veins.
It may be necessary to repeat embolisation for other veins through the same opening and using the same catheter and microcatheter combination.
When all abnormal veins are treated, introducer sheath is removed, and the Surgeon will press on the small puncture site for about 5 minutes to prevent any bleeding.